
Für eine deutsche Übersetzung dieser Seite einfach die Brandenburger Flagge anklicken
 |
Click the Brandenburg Flag for a German translation Für eine deutsche Übersetzung dieser Seite einfach die Brandenburger Flagge anklicken |


|
|
Space FirstsA listing of pioneering achievements |
|


|
March 16, 1926
|
 |
Nell
First modern rocket
|

|
June 11, 1928
|
 |
Lippisch Ente
First rocket-powered aircraft
|

|
February 2, 1931
|
 |
Experimental Rocket 7
First commercial use of a rocket
|

|
June 20, 1939
|
 |
Heinkel He 176
First rocket-plane
|


|
October 3, 1942
|
 |
A4 Launch #4
First human made object to reach the boundaries of space
|


|
June 20, 1944
|
 |
A4 Launch #48
First object to reach space by modern standards
|


|
March 1, 1945
|
 |
Bachem Ba 349 M23
First manned rocket flight
|

|
October 24, 1946
|
 |
V-2 No. 13
First picture of Earth from space.
|

|
February 20, 1947
|
 |
Blossom 1
First animals in space.
|

|
October 14, 1947
|
 |
XS-1 No. 50
First manned supersonic rocket plane.
|

|
June 14, 1949
|
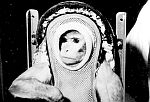 |
V-2 No. 45
First mammal in space.
|

|
July 22, 1951
|
 |
R-1V No. 1
First mammals safely returned from space.
|

|
February 21, 1954
|
 |
Véronique NA - Test Flight No. 2
First Rocket not launched by a superpower to reach space
|

|
August 21, 1957
|
 |
R-7 M1-9 (I-3) test
First successful ICBM launch
|

|
October 4, 1957
|
 |
Sputnik 1
First artificial satellite
|

|
November 3, 1957
|
 |
Sputnik 2
First animal in earth orbit.
|

|
February 1, 1958
|
 |
Explorer 1
First outer space discovery
|

|
March 17, 1958
|
 |
Vanguard 1
First satellite equipped with solar cells
|

|
January 2, 1959
|
 |
Luna 1
First probe to leave earth orbit.
|

|
August 7, 1959
|
 |
Explorer 6
First pictures of the earth from orbit.
|

|
September 13, 1959
|
 |
Luna 2
First probe to reach the Moon.
|

|
October 4, 1959
|
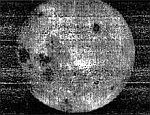 |
Luna 3
First pictures of moon's far side.
|

|
April 1, 1960
|
 |
TIROS 1
First weather satellite
|

|
April 13, 1960
|
 |
Transit 1B / GRAB-Dummy
First launch of multiple satellites with one rocket |

|
August 11, 1960
|
 |
Discoverer 13 (Corona 13)
First recovery of an object from orbit.
|

|
August 12, 1960
|
 |
Echo 1
First (passive) communications satellite
|

|
August 20, 1960
|
 |
Korabl-Sputnik 2
First successful return of animals from orbit
|

|
August 12, 1960
|
 |
Mercury-Redstone 2
First Hominid in Space
|

|
February 12, 1961
|
 |
Venera 1
First launch from park orbit into heliocentric orbit
|

|
April 12, 1961
|
 |
Vostok 1
First human in space
|

|
May 5, 1961
|
 |
Freedom 7
First human to return to earth in a spacecraft
|

|
August 6, 1961
|
 |
Vostok 2
First crewed mission lasting a full day
|

|
March 16, 1962
|
 |
Kosmos 1
The first of 2551 (and counting)
|

|
April 26, 1962
|
 |
Ranger 4
First spacecraft to impact on the far side of the moon
|

|
April 26, 1962
|
 |
Ariel 1
First Satellite not built by a superpower
|

|
July 7, 1962
|
 |
Telstar 1
First active communications satellite
|

|
August 11/12, 1962
|
 |
Vostok 3 / Vostok 4
First simultaneous flight of two crewed spacecrafts
|

|
December 14, 1962
|
 |
Mariner 2
First successful planetary flyby
|

|
June 16, 1963
|
 |
Vostok 6
First woman in space
|

|
July 19, 1963
|
 |
X-15; Flight 90
First space plane
|

|
November 1, 1963
|
 |
Polyot 1
First maneuverable satellite
|

|
December 5, 1963
|
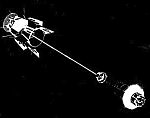 |
Transit 5BN-2
First operational navigation satellite
|

|
February 2, 1964
|
 |
Echo 2
First joint US/British/Soviet space experiment
|

|
August 19, 1964
|
 |
Syncom 3
First geostationary satellite
|

|
October 12, 1964
|
 |
Voskhod 1
First multi-person crew
|

|
March 18, 1965
|
 |
Voskhod 2
First space walk
|

|
March 23, 1965
|
 |
Gemini 3
First maneuverable manned spacecraft
|

|
April 4, 1965
|
 |
Snapshot
First nuclear powered spacecraft
|

|
July 15, 1965
|
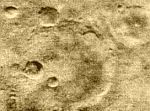 |
Mariner 4
First closeup pictures of Mars
|

|
August 21, 1965
|
 |
Gemini 5
First space flight lasting more than a week
|

|
November 26, 1965
|
 |
Asterix
First Satellite not launched by a superpower
|

|
December 15, 1965
|
 |
Gemini 6A / Gemini 7
First orbital rendezvous
|

|
February 3, 1966
|
 |
Luna 9
First soft landing on another celestial body
|

|
March 1, 1966
|
 |
Venera 3
First spacecraft to reach another planet
|

|
March 16, 1966
|
 |
Gemini 8 / GATV-5003
First orbital docking
|

|
April 3, 1966
|
 |
Luna 10
First artificial satellite to orbit the Moon
|

|
June 10, 1967
|
 |
Breaking down ethnic Barriers
 In June 1967, the US Air Force selected four new astronaut candidates for its MOL project. One of the candidates was Robert H. Lawrence Jr., the first African-American astronaut who proudly stated that he would not "sit in the back" of the spaceship. Unfortunately, Lawrence died in a plane crash before he was able to go to space. |

|
October 30, 1967
|
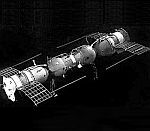 |
Cosmos 186 / Cosmos 188
First remote controlled docking in orbit
|

|
November 17, 1967
|
 |
Surveyor 6
First (brief) liftoff from the Lunar surface
|

|
November 26, 1967
|
 |
WRESAT
First Satellite Launch from the southern Hemisphere
|

|
September 18, 1968
|
 |
Zond 5
First successful circumlunar mission
|

|
December 7, 1968
|
 |
Stargazer
First space telecope
|

|
December 24, 1968
|
 |
Apollo 8
First human space flight beyond Earth orbit
|

|
January 16, 1969
|
 |
Soyuz 4 / Soyuz 5
First crew exchange in orbit
|

|
July 21, 1969
|
 |
Apollo 11
First humans to walk on the Moon
|

|
October 13, 1969
|
 |
Soyuz 6, Soyuz 7, Soyuz 8
First formation flight of three manned spacecrafts
|

|
September 24, 1970
|
 |
Luna 16
First automatic sample return from the Moon
|

|
October 3, 1970
|
 |
DIAL-Mika / DIAL-Wika
First Satellite Launch from South America
|

|
November 23, 1970
|
 |
Lunokhod 1
First remote controlled rover on another celestial body
|

|
December 15, 1970
|
 |
Venera_7
First soft landing on another planet
|

|
June 6, 1971
|
 |
Salyut 1
First manned space station
|

|
July 31, 1971
|
 |
Apollo 15
First mobile vehicle driven by humans on the Moon
|

|
November 14, 1971
|
 |
Mariner 9
First probe to orbit another planet
|

|
November 27, 1971
|
 |
Mars 2
First probe to reach Mars
|

|
December 2, 1971
|
 |
Mars 3
First soft landing on Mars
|

|
March 3, 1972
|
 |
Pioneer 10
First space craft launched with escape trajectory away from the Solar System
|

|
February 5, 1974
|
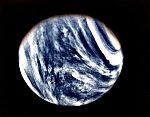 |
Mariner 10
First Swingby / First pictures of Venus
|

|
March 29, 1974
|
 |
Mariner 10
First Mercury flyby
|

|
December 4, 1974
|
 |
Pioneer 10
First Jupiter flyby
|

|
December 4, 1974
|
 |
Helios 1
First Sun observatory
|

|
July 17, 1975
|
 |
Apollo–Soyuz Test Project
First international manned space flight
|

|
October 22, 1975
|
 |
Venera 9
First picture from the surface of another planet
|

|
July 20, 1976
|
 |
Viking 1
First pictures from the surface of Mars
|

|
March 2, 1978
|
 |
Soyuz 28
First international space ship and space station crew
|

|
November 20, 1978
|
 |
International Cometary Explorer
First spacecraft placed in a halo orbit
|

|
September 1, 1979
|
 |
Pioneer 11
First Saturn flyby
|

|
July 23 & Sept. 18, 1980
|
 |
Soyuz 37; Soyuz 38
Flying across ethnical Boundaries
|

|
12 April 1981
|
 |
Columbia STS-1
First reusable manned spacecraft
|

|
February 7, 1984
|
 |
Challenger STS-41-B
First untethered spacewalk
|

|
April 11, 1984
|
 |
Challenger STS-41-C / SolarMax
First repair of a satellite in space
|

|
July 25, 1984
|
 |
Soyuz T-12 / Salyut 7
First EVA by a woman
|

|
June 11, 1985
|
 |
Vega Balloons
First balloons in the atmosphere of another planet
|

|
September 11, 1985
|
 |
International Cometary Explorer
First rendezvous with a comet
|

|
January 24, 1986
|
 |
Voyager 2
First Uranus flyby
|

|
March 14, 1986
|
 |
Halley Armada
First cluseup investigation of a comet
|

|
May 6, 1986
|
 |
Mir / Soyuz T-15 / Salyut 7
First manned transfer between two space stations
|

|
September 19, 1988
|
 |
Ofeq 1
First retrograde satellite
|

|
December 21, 1988
|
 |
Soyuz TM-4 / Mir / Soyuz TM-6
First year-long human space flight
|

|
August 8, 1989
|
 |
Hipparcos
First space telescope operating in visible light
|

|
August 25, 1989
|
 |
Voyager 2
First Neptune flyby
|

|
March 18, 1990
|
 |
Hiten
First Moon probe not launched by a super power
|

|
August 10, 1990
|
 |
Magellan
First global mapping of Venus
|

|
October 29, 1991
|
 |
Galileo
First close asteroid flyby
|

|
August 28, 1993
|
 |
Galileo
First discovery of an asteroid's moon
|

|
December 7, 1995
|
 |
Galileo-Probe
First object to enter Jupiter's atmosphere
|

|
December 8, 1995
|
 |
Galileo
First satellite in orbit of Jupiter
|

|
July 4, 1997
|
 |
Pathfinder / Sojourner
First automatic rover on Mars
|

|
February 14, 2000
|
 |
NEAR Shoemaker
First probe to orbit an asteroid
|

|
October 31, 2000
|
 |
Soyuz TM-31 / ISS
First long duration crew at the ISS
|

|
February 12, 2001
|
 |
NEAR Shoemaker
First landing on an asteroid
|

|
October 15, 2003
|
 |
Shenzhou 5
First manned space flight not launched by a superpower
|

|
June 21, 2004
|
 |
SpaceShipOne flight 15P
First non-governmental space flight
|

|
July 1, 2004
|
 |
Cassini
First satellite in orbit of Saturn
|

|
September 8, 2004
|
 |
Genesis
First sample return from beyond the Earth/Moon system
|

|
January 14, 2005
|
 |
Huygens
First soft landing on an object in the outer Solar System
|

|
July 4, 2005
|
 |
Deep Impact
First object to impact on a comet
|

|
June 14, 2010
|
 |
Hayabusa
First sample return from the Asteroid Belt
|

|
March 18, 2011
|
 |
Messenger
First spacecraft to orbit Mercury
|

|
August 25, 2012
|
 |
Voyager 1
First probe to enter interstellar space
|

|
August 6, 2014
|
 |
Rosetta
First spacecraft to orbit a comet
|

|
November 12, 2014
|
 |
Philae
First soft landing on a comet
|

|
March 6, 2015
|
 |
Dawn
First spacecraft to orbit a dwarf planet
|

|
April 30, 2015
|
 |
Messenger
First probe to impact on Mercury
|

|
July 14, 2015
|
 |
New Horizons
First Pluto flyby
|

|
April 8, 2016 March 30, 2017
|
 |
SpaceX CRS-8 / SES-10
First return and reuse of a rocket stage
|

|
February 15, 2017
|
 |
PSLV Launch C37
First deployment of over 100 satellites with one rocket
|

|
September 15, 2017
|
 |
Cassini
First probe to enter Saturn's atmosphere
|

|
September 21, 2018
|
 |
Minerva-II
First moving vehicles on an asteroid
|

|
January 1, 2019
|
 |
New Horizons
First flyby at a Kuiper Belt Object
|

|
January 3, 2019
|
 |
Chang'e 4
First automatic landing on the far side of the Moon
|

|
May 30, 2020
|
 |
Crew Dragon Demo 2
First crewed orbital flight launched by a private enterprise.
|

|
December 5, 2020
|
 |
Chang'e 5
First automatic docking in Lunar orbit.
|

|
April 19, 2021
|
 |
Ingenuity
First controlled flight on another planet
|


|
Back to Space Page |
Back to English Main Page |
 Back to Start Page |