Wikipedia
R.H. Allen:
Star Names
Ian Ridpath:
Star Tales
Universe Guide
Sea and Sky:
Constellations
IAU
Map
NASA:
Constellations
|
Wikipedia |
R.H. Allen: Star Names |
Ian Ridpath: Star Tales |
Universe Guide |
Sea and Sky: Constellations |
IAU Map |
NASA: Constellations |


|
|
ConstellationsSagittariusThe Archer |
|


|
Sagittarius is a Zodiac constellation in the
southern celestial hemisphere. Sagittarius has been know as a constellation even prior to Greek mythology. It is one of the 48 original Ptolemaic Constellations. Its name is Latin for "archer", and it is commonly represented as a centaur pulling back a bow.
|
 Scorpius in the Night Sky
Scorpius in the Night Sky
|


 Star maps based on map provided by
Sea & Sky
Star maps based on map provided by
Sea & Sky |
 |


The stars of Sagittarius |
| Number |
Desig- nation |
Name | Number |
Desig- nation |
Name | |
| 16 | ε |
Kaus Australis | 26 | ο | Omicron Sagittarii | |
| 17 | σ |
Nunki | 27 | μ | Polis | |
| 18 | ζ |
Ascella | 28 | ρ1 | Rho1 Sagittarii | |
| 19 | δ |
Kaus Media | 29 | β1 | Arkab Prior | |
| 20 | λ |
Kaus Borealis | 30 | α | Rukbat | |
| 21 | π |
Al Baldah | 31 | ι | Iota Sagittarii | |
| 22 | γ2 |
Alnasl | 32 | β2 | Arkab Posterior | |
| 23 | η |
Rabi al Warida | 33 | θ1 | Theta1 Sagittarii | |
| 24 | φ |
Awal al Sadira | 34 | ω | Terebellum | |
| 25 | τ |
Rabi al Sadira | 35 | ν1 | Ain al Rami |


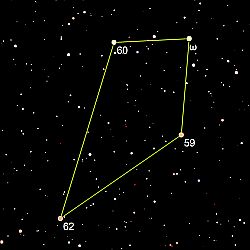
 Asterisms in Sagittarius Asterisms in SagittariusSagittarius contains one of the most popular asterisms: Teapot and Milk Dipper. We have dedicated an extra page to this formation. There is also an asterism called Terebellum derived from the Greek tetrapleuron, used by Ptolemy for a small quadrangle of stars on the hind quarter of the figure of the horse in Sagittarius. German astronomer Bayer transferred tetrapleuron into the Low Latin Terebellum. |
 Teapot;
Source:Wikipedia
Teapot;
Source:Wikipedia
|
 Terebellum;
Source:Wikipedia
Terebellum;
Source:Wikipedia
|
The asterism Terebellum consisted of ω Sagittarii and the faint stars
59,
60 and
62 Sagittarii.
 In In 2017, the IAU's Working Group on Star Names approved the name Terebellum exclusively for ω Sagittarii.  Sources: Constellation of Words, Wikipedia |


In 1771, French astronomer and comet hunter Charles Messier published a list of
diffuse objects that were not comets, to help comet hunters to distinguish between permanent and transient visually diffuse objects.
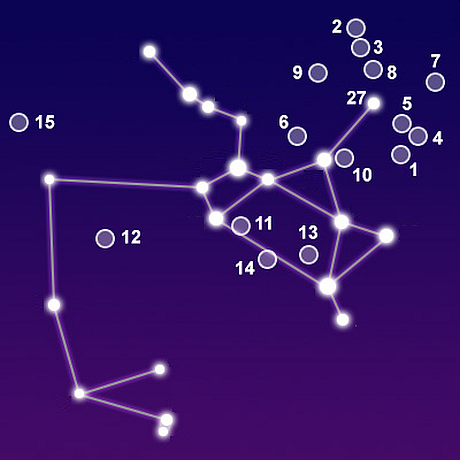
 The Messier Catalogue contains 103 star clusters, nebulae and galaxies. Fifteen of these Messier objects are located within the boundaries of the constellation Sagittarius.  Ian Ridpath explains that "...Sagittarius contains dense Milky Way star fields that lie towards the centre of our Galaxy.  The exact center of the Galaxy is believed to be marked by a radio-emitting source that astronomers call Sagittarius A, near the border with Ophiuchus."  In addition to the Messier objects, Universe Guide list another eight deep space objects that are not visible to the naked eye. |
 Star maps based on map provided by
Sea & Sky
Star maps based on map provided by
Sea & Sky |


Messier Objects in Sagittarius |
| Number |
Desig- nation |
Name | Number |
Desig- nation |
Name | |
| 1 | M8 |
Lagoon Nebula | 9 | M25 | Messier 25 / IC 4725 | |
| 2 | M17 |
Omega Nebula | 10 | M28 | Messier 28 / NGC 6626 | |
| 3 | M18 |
Messier 18 / NGC 6613 | 11 | M54 | Messier 54 / NGC 6715 | |
| 4 | M20 |
Trifid Nebula | 12 | M55 | Messier 55 / NGC 6809 | |
| 5 | M21 |
Messier 21 / NGC 6531 | 13 | M69 | Messier 69 / NGC 6637 | |
| 6 | M22 |
Sagittarius Cluster | 14 | M70 | Messier 70 / NGC 6681 | |
| 7 | M23 |
Messier 23 / NGC 6494 | 15 | M75 | Messier 75 / NGC 6864 | |
| 8 | M24 |
Sagittarius Star Cloud |


|
Back to Star Lore |
Back to Astronomy |
Back to Space Page |
Back to English |
 Back to Start Page |